What you should know about Colon Cancer
Colon cancer is a cancer of the digestive tract that affects the colon or the large intestine. The large intestine is the part of the digestive tract where water is absorbed from food remnants before it is passed to the rectum and anus for excretion.

Colon cancer is the third most diagnosed cancer all over the world with majority of cases seen in people who are 50 and above but cases have also been reported even in younger populations.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
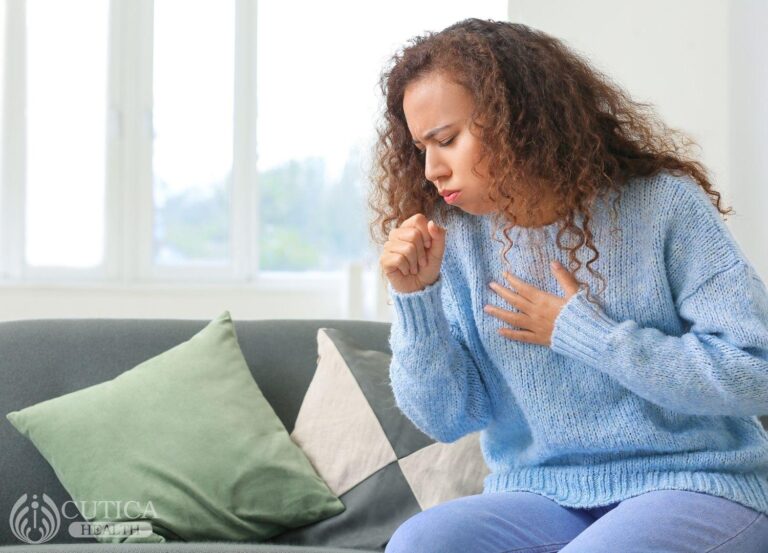
Colon cancer can give different types of symptoms, some subtle, others overt. These symptoms are dependent on the severity of the disease and the health status of the individual involved. Symptoms include a change in bowel habits which persists, including diarrhoea or constipation or a change in the consistency of stool, weakness or fatigue, unexplained weight loss, persistent abdominal discomfort, such as cramps, gas or pain and a feeling that the bowel doesn’t empty completely. Overt signs include rectal bleeding or blood in your stool, abdominal swelling.

The importance of noting these symptoms is to alert individuals to the possibility of a cancer diagnosis and prompt adequate response which is to see a physician as soon as possible for medical assessment. These symptoms raise the possibility of a cancer diagnosis but are not enough to make a diagnosis, hence medical evaluation is essential.
Risk Factors for Colon Cancer
Factors that put you at risk of colon cancer include:

- A family history of colon cancer
- Unhealthy diets (low-fiber, high-fat diet)
- Older age (>50 years)
- Being black, African-American race
- A history of colonic polyps, inflammatory intestinal conditions.
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the colon (such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease), inherited syndromes (familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and Lynch syndrome)
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Heavy use of alcohol and being exposed to radiation.
These risk factors increases risk for colon cancer as well as other cancers and it’s important that individuals note them and bring them to the barest minimum if not avoid them totally.
How is Colon Cancer treated?

Treatment is varied with different modalities used either singly or in combination. Surgical removal of the affected part and use of anti-cancer drugs are the main modes of treating colonic cancer. Seeing an expert physician will ensure the right steps are taken. These treatment guidelines have been shown to provide remission of symptoms and sometimes even cure when treatment commences early on in the disease.
While the prognosis of colon cancer is described as “guarded” (outcome in doubt), it is important to note that if colon cancer is caught early, cure is attainable but late presentation is a cause of poor outcome in individuals. Therefore, being aware of the symptoms and risk factors for colonic cancer helps quick suspicion and early intervention.