Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
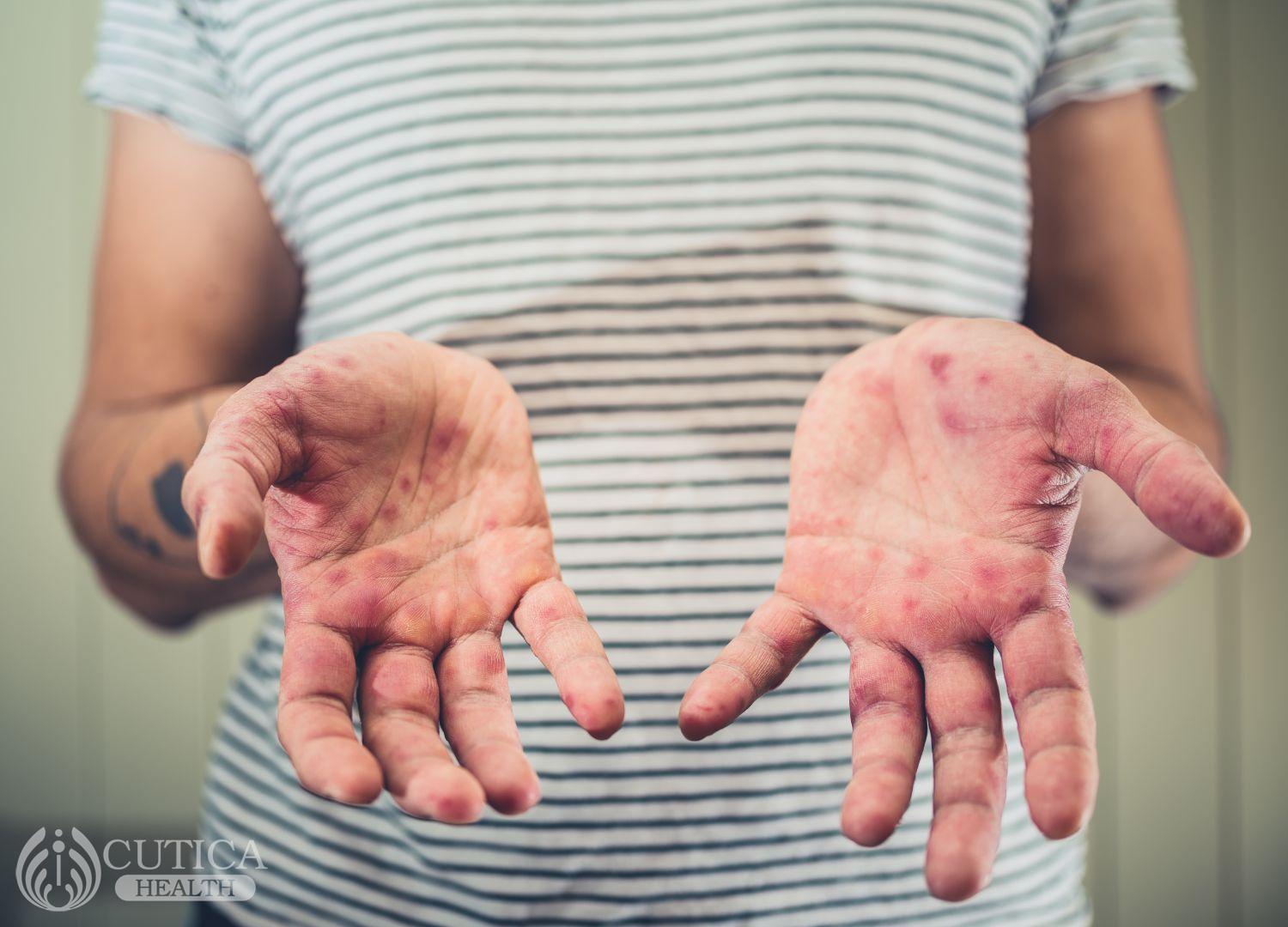
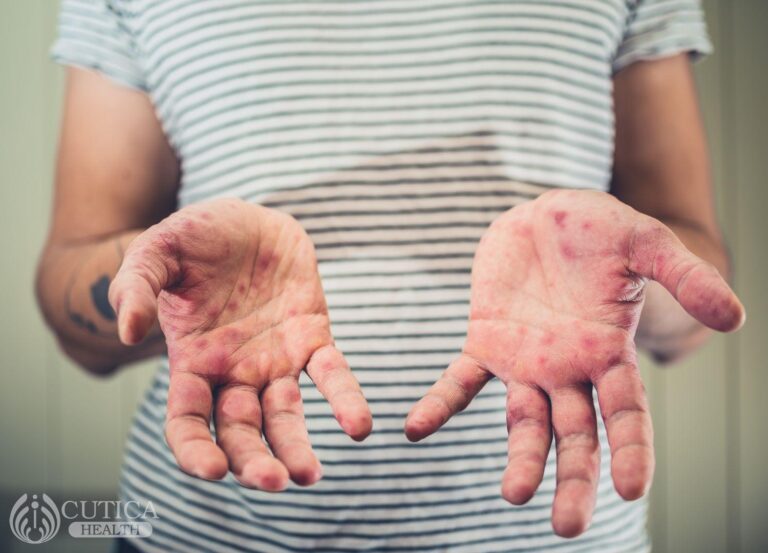
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood infection that comes with sores around or inside the mouth, and rashes or blisters on the hands, feet, buttocks, and legs. The infection is caused by a group of viruses that are highly contagious. While the infection may come with very painful rashes, it is often self-limiting and nothing serious.
What causes Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease?
The infection is most commonly caused by coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71. These viruses are found in the body fluids of an infected person, including saliva, respiratory droplets, fluid from the blisters and sores, and poop. Therefore, these viruses can be transmitted in the following ways:

Coughing or sneezing
- Close contact with body fluids of an infected person, including hugging, kissing, sharing spoons or cups
- Contact with contaminated surfaces
- Contact with poop of an infected person
While HFMD can occur at any age, it is more common in young children and during summer and fall.
Symptoms of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Common symptoms of the infection include:
- Fever
- Painful sores and blisters in the child’s mouth and around the knees, elbows, and legs
- Feeling unwell
- Loss of appetite
The sores in the mouth are often so painful; it makes eating and drinking difficult.
Treatment of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease has no cure or vaccine. The viruses often run their course and go away after 7 to 10 days. However, the following could help improve your child’s symptoms:
- Over-the-counter pain killers. It is best to avoid aspirin during this time as it could cause serious complications in children with febrile rashes.
- Cold treats like ice cream and yogurt. Try to avoid juice as these contain acids that irritate the sores
- Anti-itch creams or medicines
- Cold compresses could also lessen the symptoms. Apply ice packs or towel dipped in cold water to soothe irritating rash.

Complications of Hand Foot, and Mouth Disease
Serious complications can occur in rare cases. Some of these include:
- Dehydration, as the child may find it difficult taking fluids
- Infection of the brain, called encephalitis
- Infection of the covering of the brain, called meningitis
- Paralysis

How to Prevent Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
HFMD is contagious in the first 7 days of the illness. Here are ways to prevent spreading the infection:

Hand washing: It is important to wash your hands with soap and water regularly, especially after coming in contact with body fluids of another person.
- Cough hygiene: Use a tissue to cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze, and discard it. You can also use your elbows to cover your nose and mouth when you cough or sneeze
- Don’t hug or kiss someone with HFMD
- If you or your children have symptoms, keep away from work or school until the symptoms have resolved.